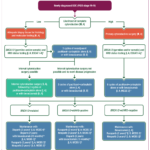
L’International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) ha pubblicato le linee guida sulla gestione dell’emorragia postpartum.
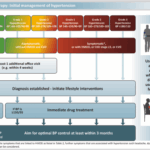
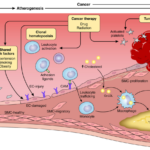
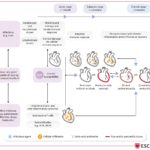
L’emorragia postpartum (PPH) continua a essere la principale causa di morbilità e mortalità materna nella maggior parte dei paesi del mondo. Nonostante i molteplici sforzi di collaborazione a tutti i livelli, c’è ancora una mancanza di attuazione o adesione alle raccomandazioni per la gestione della PPH di fronte a questa emergenza ostetrica.
“Questo documento rappresenta una revisione critica della letteratura e delle intuizioni di esperti globali sull’approccio quotidiano alla prevenzione e al trattamento della PPH. Questo lavoro aiuterà a salvare la vita delle madri, garantire un parto più sicuro e promuovere il nucleo familiare a livello globale” – afferma il Professor Anwar Nassar, Università americana di Beirut, Libano.
Scarica e leggi il full text dell’articolo:
- FIGO recommendations on the management of postpartum hemorrhage 2022
Escobar, MF, Nassar, AH, Theron, G et al.
Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2022; 157(Suppl. 1): 3– 50. doi:10.1002/ijgo.14116
Fonte: International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO)
Articoli correlati:
- Guideline Summary: WHO recommendation for using uterine balloon tamponade to treat postpartum hemorrhage.
- Meta-analysis: Oxytocin used as first‐line treatment of postpartum hemorrhage probably is more effective than misoprostol with less side‐effects. The evidence for most other uterotonic agents is limited.
- [Abstract Only] Meta-Analysis: Uterine Balloon Tamponade for the Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage
- Editorial: WHO Recommendations on Uterotonics for Postpartum Hemorrhage Prevention: What Works, and Which One?
- Consensus Statement: Prevention and Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage
- WHO Guideline: Uterotonics for the Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage