Frattura del femore prossimale nell’anziano
OrtopediaE’ stata pubblicata a cura del Sistema Nazionale Linee Guida SNLG la linea guida sulle fratture del femore prossimale nell’anziano....
ESC 2021: diagnosi e trattamento dell’insufficienza cardiaca acuta e cronica (scompenso cardiaco acuto e cronico)
CardiovascolareSono stati pubblicati i “Dieci comandamenti” delle Linee guida ESC 2021 per la diagnosi e il trattamento dello scompenso cardiaco acuto...
Nuova strategia per trasformare l’immunoterapia contro il cancro al fegato
Notizie dalla RicercaNegli ultimi anni, l’immunoterapia dei tumori è emersa come un approccio oncologico molto promettente e molto pubblicizzato. Si basa...
Valutazione e la diagnosi del dolore toracico
CardiovascolareLa prima linea guida clinica dell’ACC e dell’American Heart Association (AHA) che si concentra esclusivamente sulla valutazione e la...
La FDA approva il sistema di riabilitazione dell’ictus
Notizie dalla RicercaLa FDA ha approvato il Vivistim System, un sistema di riabilitazione senza farmaci che utilizza la stimolazione del nervo vago per il...
Gestione medica della frattura dell’anca acuta
OrtopediaI tassi di morbilità e mortalità associati alla frattura dell’anca acuta rimangono elevati. La gestione della frattura dell’anca si...
Tromboembolismo venoso (TEV) e arterioso nei pazienti con cancro
CardiovascolareIl tromboembolismo venoso (TEV), compresa la trombosi venosa profonda e l’embolia polmonare, rappresenta una delle principali cause di...
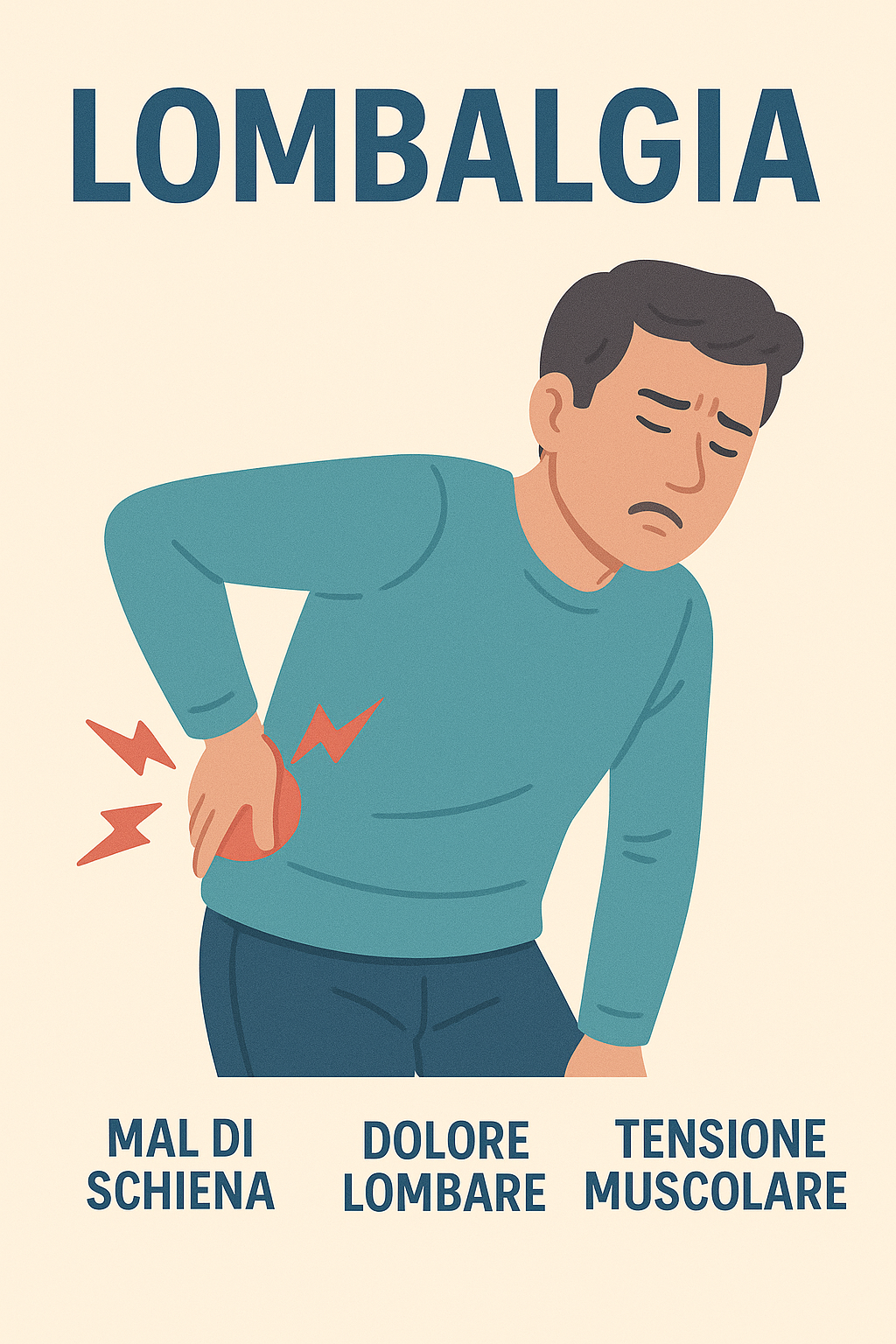
Lombalgia o mal di schiena
Schede sintetiche di patologia per i pazientiCHE COS’È E COME SI PRESENTA? E’ un dolore nella regione lombare, ossia nella parte bassa della schiena. Se è presente anche un...
Antistaminico di prima generazione (Difenidramina)
Criteri di BeersFarmaci: Difenidramina Raccomandazione d’uso: Evitare salvo per il trattamento acuto di gravi reazioni allergiche Razionale: L’uso...
Diagnosi e gestione della fibrillazione atriale
CardiovascolareQuesta linea guida di NICE copre la diagnosi e la gestione della fibrillazione atriale negli adulti. Comprende indicazioni su come fornire...
Nota 4 AIFA
Note AIFAFarmaci in nota: duloxetina, gabapentin, pregabalin Riferimenti: https://www.aifa.gov.it/nota-4 La prescrizione a carico del SSN è...
Nota 55 AIFA
Note AIFAFarmaci in nota: Tobramicina, Piperacillina + Tazobactam, Piperacillina, Netilmicina, Mezlocillina, Gentamicina, Ceftazidima, Cefepime,...
Gestione della diverticolite del colon
Gastroenterologia ed EpatologiaLa diverticolite del colon è una malattia gastrointestinale comune e caratterizzata da un esordio acuto di dolore addominale spesso grave....
Nota 87 AIFA
Note AIFAFarmaci in nota: Oxibutinina, Solifenacina, Tolterodina Riferimenti: https://www.aifa.gov.it/nota-87 Farmaci per l’incontinenza urinaria...
Nota 91 AIFA
Note AIFAFarmaci in nota: Febuxostat Riferimenti: https://www.aifa.gov.it/nota-91 Determinazione 2 novembre 2010 (GU 12 novembre 2010, n. 265):...
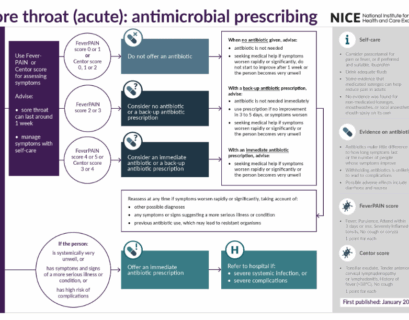
Mal di gola (acuto): trattamento con terapia antibiotica
Flow-chart TerapeuticheRiferimenti: Sore throat (acute): antimicrobial prescribing NICE guideline NG84 Published date: 26 January 2018...