Progressi nella comprensione delle Neuropatie Periferiche
Notizie dalla RicercaLe neuropatie periferiche sono una delle cause principali di dolore e disabilità in tutto il mondo. Queste condizioni possono essere:...
Diagnosi e gestione della psoriasi
DermatologiaSono state pubblicate a cura di NICE le linee guida sulla valutazione e gestione della psoriasi negli adulti, nei giovani e nei bambini. Il...
Microalbuminuria: come raccogliere correttamente le urine
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Il giorno precedente la raccolta bere circa un litro d’acqua, evitare intensi sforzi fisici e abbondante consumo di carni e formaggi; non...
Informazioni per il paziente con dislipidemia
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Perché è stato importante valutare il colesterolo? Livelli elevati di colesterolo non danno direttamente alcun disturbo. La presenza di...
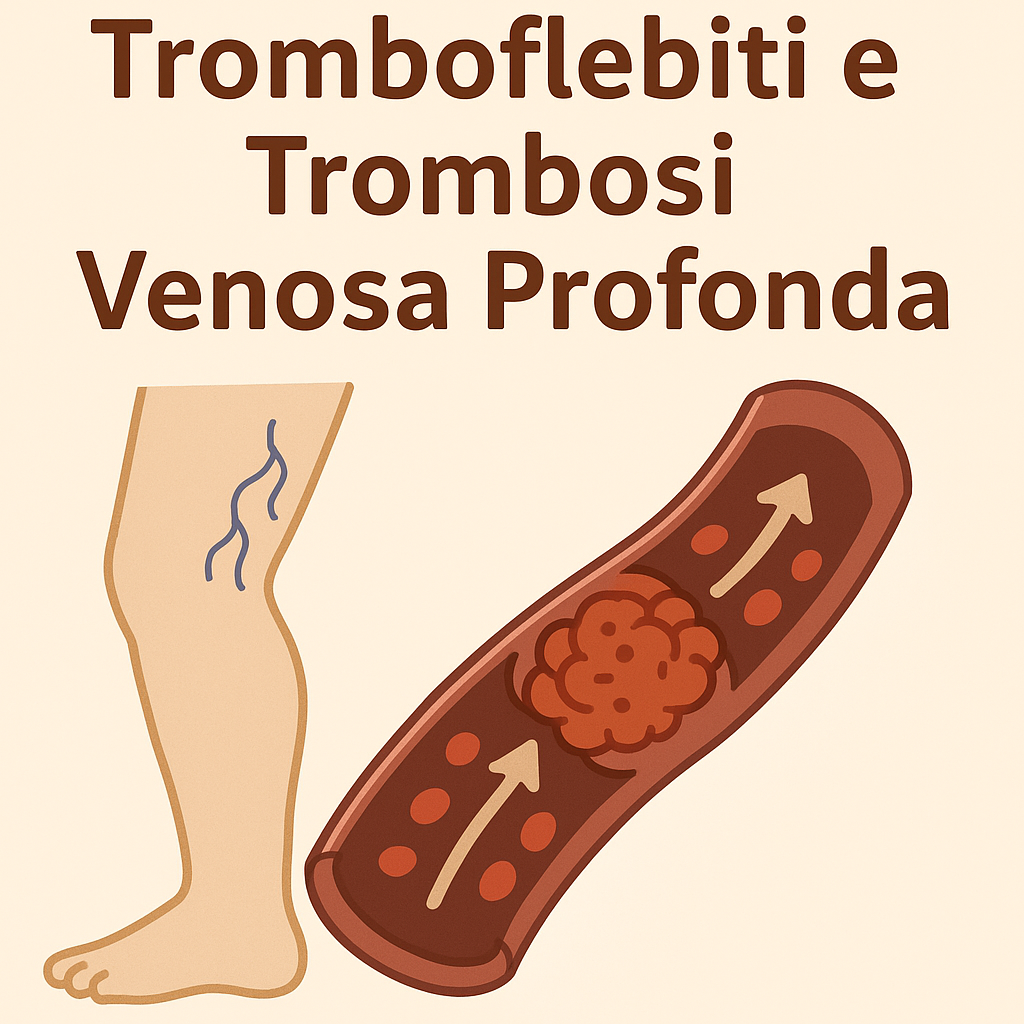
Tromboflebiti e trombosi venosa profonda (TVP)
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Per flebite si intende una infiammazione della parete di una vena, questo evento si può associare alla formazione di un trombo che...
Le infezioni genitali nella donna
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Uretriti nella donna L’uretrite causata da infezioni sessualmente trasmesse nella donna si manifesta con dolore alla minzione, spesso si...
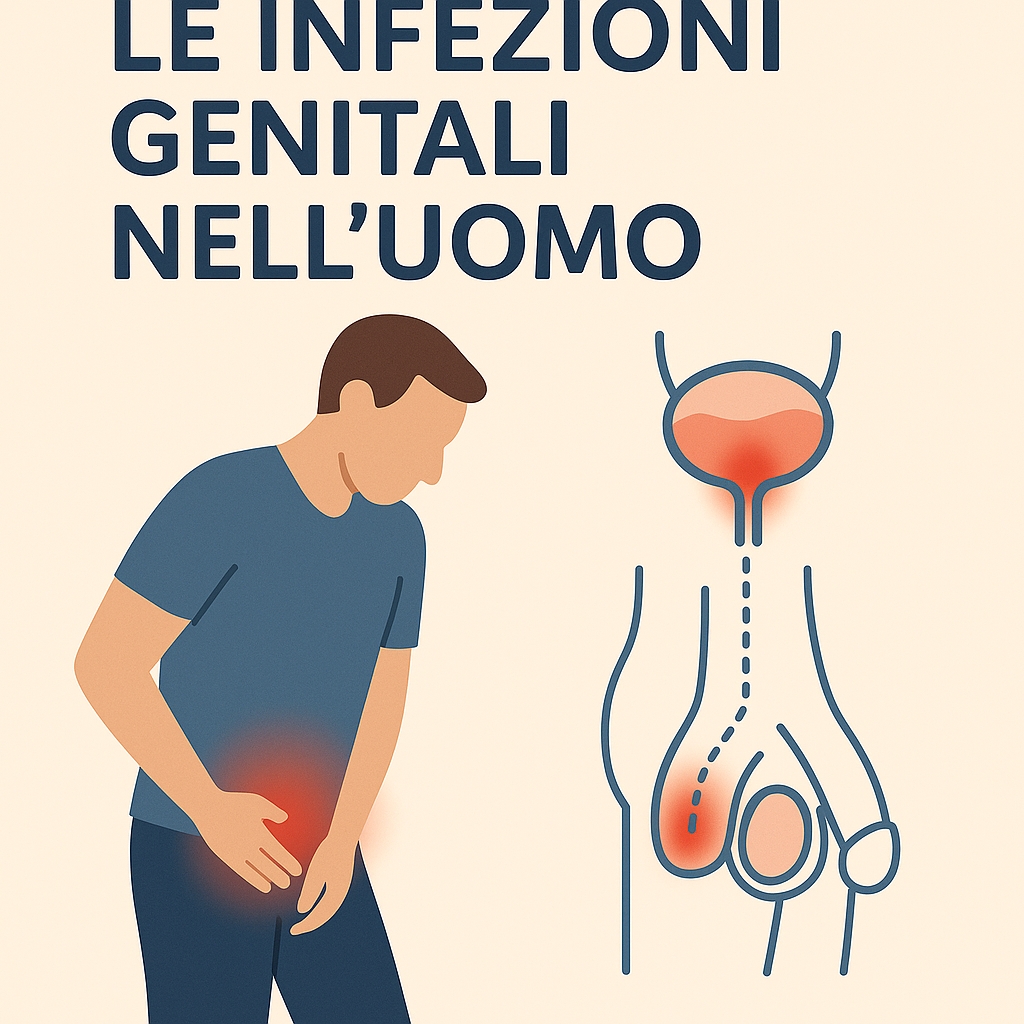
Uretrite nell’uomo
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Come si manifesta? L’uretrite nell’uomo si manifesta con perdita di materiale purulento dall’uretra, bruciore e dolore. Cause Le...
Allergie
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)L’allergia è una condizione caratterizzata da un’attivazione anomala del sistema immunitario scatenata da agenti definiti...
Tiroide e Ipertiroidismo
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)La tiroide è una ghiandola endocrina posta alla base del collo che ha l’importante funzione di produrre gli ormoni T3 e T4 sotto lo...
La bocca e i denti
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)La bocca è la porta d’ingresso dell’apparato digerente, qui avviene la prima parte della digestione, ma è anche un organo di senso....
L’uso corretto dei farmaci
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Il farmaco costituisce spesso un rimedio essenziale per la risoluzione di un problema acuto e cronico. La prescrizione è un atto medico,...
Il Sangue e la circolazione sanguigna
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Il Sangue è costituito da una parte liquida denominata plasma e da cellule: circa 5 milioni di globuli rossi, 700.000 globuli bianchi,...
I difetti della vista
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)L’occhio umano è un sistema di lenti composto di varie parti: Cornea: La finestra trasparente della sfera oculare Umore acqueo: Il...
FAQ sulla pillola anticoncezionale
Consigli pratici per i pazientiA quali esami devo sottopormi prima di iniziare una terapia ormonale per la contraccezione? Prima di cominciare una terapia ormonale è...
Colesterolo e trigliceridi
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)Il Colesterolo, cos’è? Il colesterolo è un grasso presente nel sangue che in buona parte viene prodotto dal nostro organismo, solo in...
Cefalea ed emicrania
Materiale per i pazienti (Handouts)La cefalea è un sintomo che colpisce circa il 20-40% della popolazione e viene distinta in primaria e secondaria: Cefalee primarie: non...