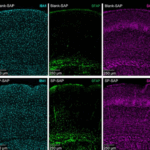
[Articles] Safety and immunogenicity of UB-612 heterologous booster in adults primed with mRNA, adenovirus, or inactivated COVID-19 vaccines: a randomized, active-controlled, Phase 3 trial
In a pivotal Phase 3 study, UB-612 demonstrated the potential for broad use as a cross-platform heterologous booster, restoring protective immunity in adults previously vaccinated with mRNA, adenovirus-vectored, or inactivated virus-based COVID-19 vaccines.
Observations from ID and Beyond: Two Pandemics Compared: Reflections on HIV and COVID-19
In HIV and ID Observations, Dr. Paul Sax compares the HIV and COVID-19 pandemics.
An Evidence-Based Approach to Covid-19 Vaccination
New England Journal of Medicine, Ahead of Print.
Linea guida sulla gestione della malattia venosa cronica
CardiovascolareLa Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) ha pubblicato una linea guida sulla gestione della malattia venosa...
Linee guida aggiornate sulla diagnosi e gestione dell’emicrania
EmicraniaQueste linee guida pubblicate da NICE, riguardano la diagnosi e la gestione della cefalea tensiva, dell’emicrania (inclusa...
Centri per la cura dei tumori ginecologici – Lombardia
Centri specialistici per la cura dei tumori ginecologiciElenco dei centri specialistici della Regione Lombardia, per la cura dei tumori ginecologici, che offrono un approccio multidisciplinare,...
Error in Key Points and Table 1
In the Original Investigation titled “Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs Sorafenib Alone in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The NRG Oncology/RTOG 1112 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial,” published online December 19, 2024, and in the February 2025 issue, there were errors in the Key Points and Table 1. In…
Nuove linee guida AHA/ACC per la gestione della malattia coronarica cronica
CardiovascolareL’American Heart Association (AHA) e l’American College of Cardiology (ACC) hanno pubblicato, sul Journal of the American College of...
Linee guida aggiornate sulle terapie emergenti nella gestione dei tumori cerebrali metastatici
Cancro al cervelloIl Congress of Neurological Surgeons ha aggiornato le linee guida per il trattamento dei tumori cerebrali metastatici, riflettendo i...
Insonnia e uso di farmaci per dormire collegati alla disabilità negli anziani
Notizie dalla RicercaL’insonnia e l’uso di farmaci per dormire sono stati collegati a un aumento del rischio di disabilità negli anziani, secondo uno...
Batteri intestinali e farmaci: interazioni inaspettate
Notizie dalla RicercaUn nuovo studio pubblicato su Nature Chemistry esplora come il microbioma intestinale possa influire sull’efficacia dei farmaci mirati ai...
Chatbot terapeutico con intelligenza artificiale produce notevoli benefici per la salute mentale
Notizie dalla RicercaI ricercatori dell’University of Dartmouth hanno condotto il primo esperimento clinico di un chatbot terapeutico basato...
Colesterolo alto: nuova terapia combinata
Notizie dalla RicercaUna meta-analisi internazionale, condotta dai ricercatori dell’Università Cattolica Giovanni Paolo II di Lublino, suggerisce che, nei...
Tumore alla prostata, una nuova cura blocca le metastasi
Notizie dalla RicercaI risultati di uno studio (RADIOSA) dell’Istituto Europeo di Oncologia, pubblicati sulla rivista “Lancet Oncology“, dimostrano che la...
Cancro al seno avanzato: diagnosi e trattamento
Cancro al senoQuesta linea guida pubblicata da NICE, riguarda l’assistenza e il supporto per le persone con tumore al seno avanzato (stadio 4). Ha lo...
Linee guida sulla degenerazione maculare legata all’età
OculisticaLa forma neovascolare della degenerazione maculare legata all’età (AMD) è responsabile della maggior parte delle gravi perdite della...