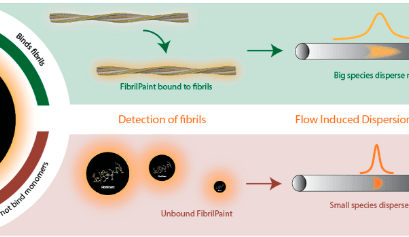
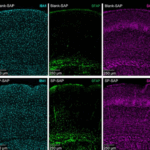
Abstract 4363027: Paradoxical Renal Protection after Euglycemic DKA in a CKD Stage 4 Diabetic Patient on Empagliflozin: A Case Report and Mechanistic Insights
Circulation, Volume 152, Issue Suppl_3, Page A4363027-A4363027, November 4, 2025. Introduction:Over the last few years, studies have demonstrated that the usage of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease has significantly reduced the risk of hospitalisation fo…
National Survey of Children’s Health Is Representative of Children, Not Mothers—Reply
In Reply In 2024, an advisory from the US Surgeon General identified parental mental health as a pressing public health issue, highlighting rising levels of parental stress. Following this advisory, our study used the National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH) to investigate recent trends and disp…
Sviluppato un metodo di analisi del sangue per rilevare precocemente la demenza
Notizie dalla RicercaLa diagnosi precoce del morbo di Alzheimer è un passo più vicina grazie a un nuovo metodo di misurazione sviluppato dai chimici...
Avvio procedimento e apertura piattaforma Pay-Back 5% – anno 2025
Si informano le aziende farmaceutiche che dalle ore 12:00 del 30 ottobre sarà attivo il servizio online “Spending-Pha” per la gestione del procedimento di payback 5% per l’anno 2025 e che è possibile presentare eventuali osservazioni entro e non oltre il 6 novembre p.v. ore 18:00.
Linee guida per il trattamento dell’apnea notturna centrale (OSA)
PneumologiaUna nuova linea guida per la pratica clinica sviluppata da una task force dell’American Academy of Sleep Medicine fornisce...
Un basso livello di colesterolo è associato a un rischio inferiore di demenza
Notizie dalla RicercaLa ricerca, condotta presso l’Università di Bristol e il Dipartimento di Biochimica Clinica dell’Ospedale Universitario di...
Iperplasia Surrenale Congenita (CAH), Linee Guida Internazionali
Senza categoriaLe linee guida 2018 dell’Endocrine Society rappresentano il riferimento principale per la diagnosi e la gestione dell’Iperplasia...
Heart Stress and Blood Pressure Management in Older Adults: Post Hoc Analysis of the ASPREE Trial
Circulation, Volume 152, Issue 23, Page 1621-1633, December 9, 2025. BACKGROUND:Blood pressure (BP) management in older adults is complex because of age-related physiological changes and uncertainty around ideal systolic BP (SBP) targets. Heart stress (HS), defined by age-adjusted elevation in NT-p…
AI contribuisce a scoprire un nuovo potenziale percorso terapeutico contro il cancro
Intelligenza Artificiale in MedicinaI ricercatori di Google e della Yale University hanno sviluppato un modello di intelligenza artificiale più “avanzato e...
Hypercontractility and Oxidative Stress Drive Creatine Kinase Dysfunction in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Circulation, Ahead of Print. BACKGROUND:Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a prevalent inherited cardiac disorder marked by left ventricular hypertrophy and hypercontractility. This excessive mechanical workload creates an energetic mismatch in which consumption exceeds production, leading to myo…
Linee guida sulla gestione del mieloma multiplo recidivante
MielomaLa British Society of Haematology ha publicato le linee guida sulla gestione del mieoloma multiplo recidivante. Nel documento si...
Nobel 2025 per la scoperta del meccanismo con cui il sistema immunitario reagisce alle infezioni
Notizie dalla RicercaIl Premio Nobel per la Medicina 2025 è stato assegnato a Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell e Shimon...
Patient and Caregiver Outcomes of Health System, Community-Based, and Usual Dementia Care
This randomized clinical trial compares the effectiveness of health system dementia care, community-based dementia care, and usual care on person living with dementia and caregiver outcomes.
Digital Well-Being Training With Health Care Professionals
This randomized clinical trial examines whether a 13- week digital well-being training could improve well-being and reduce stress among health care professionals in Mexico.